
Product Information

Carboxymethyl cellulose, or CMC, is a cellulose derivative with carboxymethyl groups (-CH2-COOH) bound to some of the hydroxyl groups of the glucopyranose monomers that make up the cellulose backbone. Carboxymethylcellulose (CMC; E466) is a derivative of cellulose formed by its reaction with alkali and chloroacetic acid.
Structural unit and Molecular structure
 |
The CMC structure is based on the ß-(1-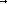 4)-D-glucopyranose polymer of cellulose. Different preparations may have different degrees of substitution, but it is generally in the range 0.6 - 0.95 derivatives per monomer unit.
4)-D-glucopyranose polymer of cellulose. Different preparations may have different degrees of substitution, but it is generally in the range 0.6 - 0.95 derivatives per monomer unit.
CMC molecules are most extended (rod-like) at low concentrations but at higher concentrations the molecules overlap and coil up and then, at high concentrations, entangle to become a thermoreversible gel. Increasing ionic strength and reducing pH both decrease the viscosity as they cause the polymer to become more coiled.
Alkali cellulose + Sodium choroacetate -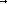 Carboxymethylcellulose sodium
Carboxymethylcellulose sodium
or expressed as follows:
C6H7O2(OH)3+XNaOH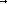 C6H7O2(OH)3·XNaOH
C6H7O2(OH)3·XNaOH
C6H7O2(OH)3·XNaOH+mCH2ClCOONa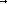
Manufacture and Quality Control Wenda® Carboxymethyl Cellulose
Purified Cotton RAW MATERIAL- Mixing -
Mixing - Kneading-
Kneading- Washing-
Washing- Centrifugation-
Centrifugation- Drying-
Drying- Milling-
Milling- Sieving-
Sieving- PACKING
PACKING
Regarding Quality Control points during and after production of Carboxymethycelulose, note that WENDA-CMC brand Carboxymethycelulose meets with FCC IV and USP, GMO-free and other international food additive standards. Products are produced in accordance with CGMP/HACCP /ISO requirements. We have the certification of ISO9001:2000, ISO22000 (HACCP), HALAL and KOSHER.
.
Rheology of Wenda® Carboxymethyl Cellulose
Sodium carboxymethycellulose or cellulose gum is available in many different viscosity grades, particle size types, and flow characteristics. It forms crystal clear solutions, is clean in flavor and is very rapid in hydration. Various combinations of these properties permit tailoring of CMC to many different food systems making this hydrocolloid a multi-tasking hydrocolloid.
CMC dissolves rapidly in cold water and mainly used for controlling viscosity without gelling (CMC, at typical concentrations, does not gel even in the presence of calcium ions). As its viscosity drops during heating, it may be used to improve the volume yield during baking by encouraging gas bubble formation. Its control of viscosity allows use as thickener, phase and emulsion stabilizer and suspending agent. CMC can be also used for its water-holding capacity as this is high even at low viscosity; particularly when used as the Ca2+ salt. Thus, it is used for retarding staling and reducing fat uptake into fried foods.
The average chain length and degree of substitution are of great importance; the more-hydrophobic lower substituted CMCs are thixotropic but more-extended higher substituted CMCs are pseudoplastic. At low pH, CMC may form cross-links through lactonization between carboxylic acid and free hydroxyl groups.
It is fairly stable over a pH range of 5.0 to 10.0 , but acidification below pH 5.0 will reduce the viscosity and stability except in a special acid - stable type of CMC. A variety of types are available which differ in viscosity and degree of substitution (the number of sodium groups per unit). The usage range is from 0.05 to 0.5 percent.
1. Add CMC portion-wise into a solvent system while stirring.
2. Add CMC portion-wise into a solvent system while heating. Optimum temperature 50°C-60°C.
3. If CMC is used in combination with other solids, disperse CMC in the solids thoroughly, and dissolve.
4. If CMC is pre-dispersed in an insoluble solvent, like ethanol or glycerine, the dissolution in water can be accelerated.
Application Guideline of Wenda® Carboxymethyl Cellulose
WENDA®CMC, Food Grade , having the characteristics of possessing;
1. Finely distributed molecular weight
2. High resistance to acid
3. High resistance to salt
4. High transparency, low free fibers
4. Low gel,
can be used for its various functions showing the below properties;
1. Thickening: CMC can produce high viscosity at low concentration. It also acts as a lubricant.
2. Water retention: CMC is a water binder, helps to increase shelf life of food.
3. Suspending aid: CMC acts as an emulsifier and suspension stabilizer, particularly in icings to control ice crystal size.
4. Film forming: CMC can produce a film on the surface of fried food, eg. instant noodle, and prevent absorption of excessive vegetable oil.
5. Chemical stability: CMC is resistant to heat, light, mold and commonly used chemicals.
6. Physiologically inert: CMC as a food additive has no caloric value and can not be metabolized.
7. Odorless, tasteless, non-toxic.
WENDA®CMC, Food Grade can be used in the following Application Fields:
Liquid beverage: Adding WENDA®CMC, into Liquid Beverage can suspend particles evenly, fix the color and extend shelf life.
Lactic acid beverage: Adding WENDA®CMC, can stabilize the solution, prevent precipitation, improve mouth feel, increase quality and thermal stablity.
Milk: mainly for soy milk, peanut milk, almond milk, etc. Adding WENDA®CMC, food grade can suspend, emulsify, stabilize the product, avoid fatty particles buildup as well as whiten, sweeten and remove soy odor.
Yogurt; Adding WENDA®CMC, stabilizes yoghurt and prevents sedimentation, increases shelf life, performs well at pH 2-4, improves mouthfeel.
Frozen foods (ice cream)
Adding WENDA®CMC, into frozen foods can control ice crystal size and improves mouthfeel, increase whiteness, enlarge volume, helps body formation of the ice cream , can mix freely with milk, sugar, emulsifier and other ingredients, brings glossy surface to the ice cream.
Wheat foods:Using WENDA®CMC, in bread can make the bread homogeneous micro-corn (e.g. honeycomb-like texture) enlarge volume, decrease crumb falling, prevent collapse and maintain freshness and moisture. The use of WENDA®CMC in noodles/instant noodles facilitates mixing and extrusion of flour, can enhance toughness, maintain length, improve fine and smooth mouth feel, forms smooth film on the surface of noodle on heating, prevents absorption of excessive vegetable oil, increases the noodle's strength and saves cost on handling.
Biscuit, Pancake and Moon-cake
In the production of biscuit and pancake, adding WENDA®CMC, into wheat flour can adjust flour flexibility, improve texture, build better shape, avoid breakage, smooth and brighten cake surface, improve crispy, taste and mouth feel.
For mooncake application, mixing WENDA®CMC, into the cake crust and cake-filling or spraying WENDA®CMC, solution onto the cake surface can inhibit molding, maintain moisture to keep soft, extend shelf life, improve outface fineness. Also make cake-filling soft, delicious as well as extend shelf life.
Sauces & Toppings
WENDA®CMC, is suitable for sauce and toppings such as peanut sauce, sesame paste, almond sauce and mixed congee, etc.
As the basic substance of sauce, WENDA®CMC, has the advantages of good solubility in cold or boiled water, good smooth taste. Moreover, it can improve taste caused by artificial sweetener. WENDA®CMC, also has much better stability than starch. WENDA® CMC, is suitable to be used as a thickener and stabilizer in seasonings like oyster sauce, soy sauce, fruit jams, chili sauce, peanut sauce and sesame sauce. Also functions to improve texture, color, smell and taste.
Application of Wenda® Carboxymethyl Cellulose
|
|
Application Field |
Recommended Grade |
|
|
Fruit products & beverage |
FL20 FL50 FL100 FM300 FH1500 |
|
|
Dairy products |
FL100 FM100 FM300 FH1500 |
|
|
Ice cream |
FH700 FH1000 FH1500 FH1800 FH2000 |
|
|
Dressings & Sauces |
FM300 FH1500 |
|
|
Instant noodle |
FH1000 FH1800 FH2000 |
|
|
Fast-dissolving food |
FM1000 FM2000 FM2500 |
|
|
Canned food |
FH1000 FH3000 |
|
|
Meat Product |
FH4000 FH5000 FH6000 |
Presentation Units and Shelf Life
|
Product Name
|
Packaging Unit
|
Packaging Type
|
Shelf Life
|
Storage Conditions
|
|
Wenda ® CMC Food Grade |
25KG/BAG
|
Multi-paper bags with PE inner |
18 months
|
Sealed and stored in dry conditions, at Room Temperature
|
-
Özsezen K.V.K.K
-
Biokim Özsezen Veri Saklama ve İmha Politikası
Biokim Özsezen Çalışan Adayı Aydınlatma Metni
Biokim Özsezen Gerçek Kişi Tedarikçi ve Tüzel Kişi Tedarikçi Yetkilisi Aydınlatma Metni
Biokim Özsezen Kamera İzleme Faaliyetine İlişkin Aydınlatma Metni
Biokim Özsezen Veri Sahibi Başvuru Formu
Biokim Özsezen Müşterilere ve Müşteri Temsilcilerine Yönelik Aydınlatma
-
Wenda K.V.K.K
-
Biokim Wenda Çalışan Adayı Aydınlatma Metni
Biokim Wenda Gerçek Kişi Tedarikçi ve Tüzel Kişi Tedarikçi Yetkilisi Aydınlatma Metni
Biokim Wenda Kamera İzleme Faaliyetine İlişkin Aydınlatma Metni
Biokim Wenda Müşterilere ve Müşteri Temsilcilerine Yönelik Aydınlatma Metni
Biokim Wenda Veri Sahibi Başvuru Formu
BiokimWenda Veri Saklama ve İ̇mha Politikası











