
Product and Raw Material Information
 Alginate is found in a wide variety of brown seaweeds and is present as a structural polysaccharide. The type of structure is influenced by the seaweed source as well as the growing conditions of the weed. The block structure ultimately dictates the gelling properties of the alginate produced. Durvillea and ascophyllum species tend to be high in mannuronic acid and hence form softer gels whereas alginate sources such as laminaria hyperborea stems tend to have a higher guluronic acid content an hence form much more rigid gels.
Alginate is found in a wide variety of brown seaweeds and is present as a structural polysaccharide. The type of structure is influenced by the seaweed source as well as the growing conditions of the weed. The block structure ultimately dictates the gelling properties of the alginate produced. Durvillea and ascophyllum species tend to be high in mannuronic acid and hence form softer gels whereas alginate sources such as laminaria hyperborea stems tend to have a higher guluronic acid content an hence form much more rigid gels.
Alginate bearing weeds are typically found in temperate or cold water. The major manufacturers are based near the weed sources in China, San Diego, Chile, Scotland, Denmark and Norway.
Bright Moon now is the largest sodium alginate manufacturer in China The primary brown seaweed utilized by Bright Moon for the extraction of alginates is Laminaria Japonica and Lessonia Nigrescens. The former is cultivated along the Coast of Shandong Peninsula in China, while the latter is imported from Chile. Bright Moon also adopts other species of seaweed like lessonia flavacans, ascophyllum nodosum, etc. To meet the special need of the customers.
Structural unit and Molecular structure
Alginate is a polysaccharide which is composed of several building units (typically 100–3000) linked together in a flexible chain. Polymers of natural origin are commonly called biopolymers.
Alginate is a linear co-biopolymer of ß-D-Mannuronic acid and 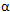 -L-Guluronic acid. Depending on the seaweed specie as well as the part of the plant, the ratio of mannuronic and guluronic acid can vary. It is also known that the block structure within the alginate can vary significantly. The poly-guluronic acid blocks bind significantly more effectively with calcium ions than the poly-mannuronic acid blocks. The weed types with the higher guluronic acid levels are normally the ones that show the strongest interaction with calcium and hence the strongest gel strength.
-L-Guluronic acid. Depending on the seaweed specie as well as the part of the plant, the ratio of mannuronic and guluronic acid can vary. It is also known that the block structure within the alginate can vary significantly. The poly-guluronic acid blocks bind significantly more effectively with calcium ions than the poly-mannuronic acid blocks. The weed types with the higher guluronic acid levels are normally the ones that show the strongest interaction with calcium and hence the strongest gel strength.
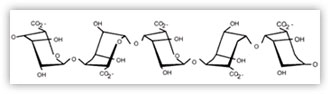
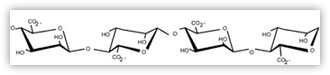
When producing alginates, uronic acid is converted into the salt-forms mannuronate (M) and guluronate (G). The G- and M- units are joined together in one of three blocks: GG.., MM.. , and MG... The proportion, distribution, and length of these blocks determine the chemical and physical properties of the alginate molecules.
|
GULURONIC ACID BLOCK
|
MANNURONIC ACID BLOCK
|
 |
 |
Manufacture and Quality Control of Alginates
There are essentially two processes for the preparation of alginates. They all start off with similar extraction procedures but vary in the methods used to precipitate the alginate at the end of the process.
These two processes are either alkali method or acid precipitation method. While alkali method is more popular in China. Also according to the neutralization process, there are also two processing technology, one is called solid phase and the other is called liquid phase. Bright Moon normally produce industrial grade alginate using solid phase method while food grade is by liquid phase method. The following diagram shows the liqquid phase method. For solid phase method, the only difference is to adopt sodium carbonate to replace ethanol and sodium hydroxide in neutralization process.

Regarding Quality Control points during and after production of Alginates, note that WENDA brand sodium alginate meets with FCC, GB1976-80 and other international food additive standards. Products are produced in accordance with CGMP/HACCP /ISO requirements. We have the certification of ISO9001:2000, ISO22000 (HACCP) and KOSHER.



