Product and Raw Material Information
 Guar is a very old cultivated plant, native to India and Pakistan. It is an annual crop and is sown at the end of July and harvested in November. The pods are 5-8 cms long and are used as a green vegetable or as a cattle feed besides the industrial extraction of Guar Gum.
Guar is a very old cultivated plant, native to India and Pakistan. It is an annual crop and is sown at the end of July and harvested in November. The pods are 5-8 cms long and are used as a green vegetable or as a cattle feed besides the industrial extraction of Guar Gum.
Guar Gum is derived from the seeds of the Guar plant "Cyamopsis Tetragonalobus".
The crop is sown after the first rains in July and harvested in late October. The pods are then sun - dried, manually separated from the seeds and supplied to the industry for processing. Tender green Guar pods are consumed as a vegetable in India.
Structural unit and Molecular structure
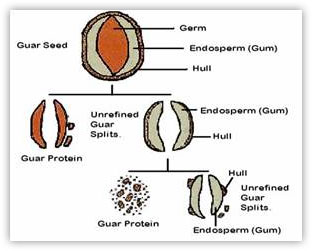
The Guar seed is dicotyledonous having a diameter of about 2.0-3.0 mm. The seeds make-up about 60%-70% of the pod weight. The germ is completely enveloped by the two halves of the endosperm which is the source of the gum. The tough seed skin or husk is of a fibrous nature, composed of compressed thin layers of cellulosic material.
So called endosperm, Guar Gum has an overall ratio of mannose to galactose of around 2: 1. The galactose substituents are regularly distributed along the mannose chain.
1 GALACTOSE UNIT FOR 2 MANNOSE RESIDUES
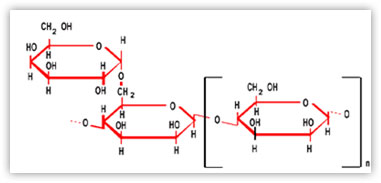
The main chain consists of (1-4) linked beta-D mannose residues and the side chain of (1-6) linked alpha-D galactose.
Manufacture and Quality Control of Guar Gum
The gum is commercially extracted from the seeds essentially by a mechanical process of roasting, differential attrition, sieving and polishing. The seeds are broken and the germ is separated from the endosperm. Two halves of the endosperm are obtained from each seed and are known as Undehusked Guar Splits. When the fine layer of fibrous material, which forms the husk, is removed and separated from the endosperm halves by polishing, Refined Guar Splits are obtained. The husk and germ are rich in protein form a valuable cattle-feed. The refined Guar Splits are then treated and finished into powders by a variety of routes and processing techniques depending upon then end product desired. High purity Guar gums for foods, feeds and pharmaceutical applications can be produced in many different viscosities, hydration rates and particle size distributions to suit specific applications. Various modified/derivatised Guar gums such as hydrolysed, hydroxyalkyl, carboxyalkyl, oxidised, sulphated, borated, cationic and various combinations of these are commercially useful for a number of industrial applications.